Acne causes & skin care with daily routine
Apr 1, 2025
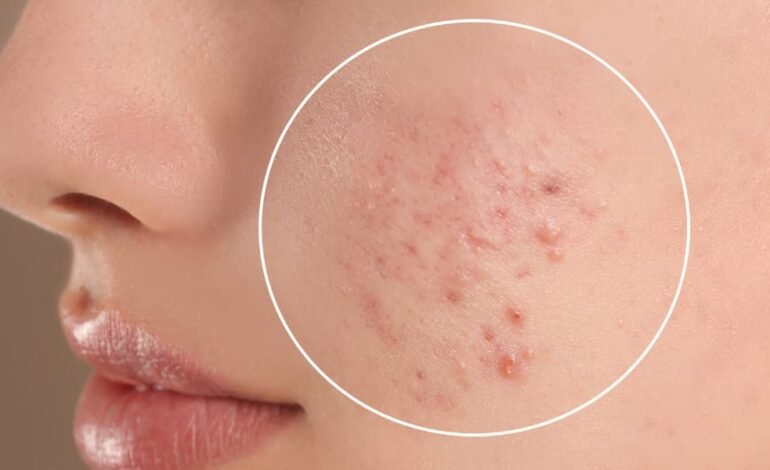
Acne is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. It primarily affects areas of the skin that have the most sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the face, chest, back, and shoulders. Acne can appear as pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, or nodules, and its severity can vary from mild to severe.
Hormonal Changes:
Diet:
Stress:
Hot and Humid Weather:
Cosmetic Products:
Certain Medications:
Friction or Pressure:
By understanding the causes, triggers, and the proper care regimen, acne can often be managed effectively. If it persists or becomes severe, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for more targeted treatment.
Causes of Acne:
- Excess Oil Production (Sebum):
- The sebaceous glands in the skin produce oil (sebum) to keep the skin lubricated. However, when these glands produce too much oil, it can clog pores, leading to acne.
- Hormonal Changes:
- Hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, pregnancy, menstruation, or when taking birth control, can increase oil production in the skin, making acne worse.
- Clogged Hair Follicles:
- Dead skin cells that are not shed properly can mix with oil and block the pores, which can lead to acne formation.
- Bacteria:
- The skin naturally contains Propionibacterium acnes bacteria, which can multiply in clogged pores, causing inflammation and infection that results in acne.
- Diet:
- Some studies suggest that certain foods, like those high in refined sugars, dairy, and greasy foods, may contribute to acne flare-ups.
- Stress:
- Stress can increase the body’s production of hormones (like cortisol), which can trigger or worsen acne.
- Medications:
- Some medications, such as corticosteroids or lithium, can contribute to acne as a side effect.
- Genetics:
- If your parents had acne, you’re more likely to develop it as well.
How to Take Care of Acne:
- Gentle Cleansing:
- Cleanse your face with a mild, non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores) cleanser twice daily to remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells. Avoid scrubbing too hard, as this can irritate the skin and make acne worse.
- Topical Treatments:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Helps kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.
- Salicylic Acid: Exfoliates the skin and helps keep pores clear.
- Retinoids (e.g., tretinoin): Help prevent clogged pores and promote skin renewal.
- Sulfur: Sometimes used to treat mild acne, as it has antibacterial properties.
- Moisturizing:
- Use a non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated, as some acne treatments can dry out your skin.
- Sun Protection:
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) every day to protect your skin from UV damage, which can worsen acne and lead to scarring.
- Avoid Touching or Picking at Acne:
- Picking or squeezing acne can push bacteria deeper into the skin, causing more inflammation and scarring.
- Regularly Wash Your Pillowcase and Towels:
- Changing pillowcases and towels often can reduce the buildup of bacteria and oils that can clog pores.
- Diet:
- Consider limiting dairy and sugary foods, as they might trigger breakouts in some people. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help improve skin health.
- See a Dermatologist:
- If over-the-counter treatments don’t work, a dermatologist may prescribe oral medications (like antibiotics, hormonal therapy, or isotretinoin) or stronger topical treatments.
Precautions:
- Avoid Over-Cleansing:
- Washing your face too frequently or using harsh cleansers can irritate the skin, leading to more breakouts.
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products:
- When choosing skincare and makeup products, look for those labeled “non-comedogenic,” meaning they are less likely to clog pores.
- Don’t Overuse Acne Treatments:
- Too many acne treatments at once can irritate the skin. Stick to one or two effective treatments.
- Protect Your Skin from the Sun:
- Acne medications (especially retinoids) can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, increasing the risk of burns and irritation.
Common Acne Triggers:
-
Puberty, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and the use of birth control can cause acne flare-ups.
-
Foods high in sugar, dairy, and processed carbs have been linked to acne in some people.
-
Emotional stress can trigger the production of cortisol, which can lead to more acne.
-
Excessive sweating from hot weather or exercise can clog pores and trigger breakouts.
-
Some makeup, lotions, and creams can clog pores, especially if they contain oils or alcohol. Always look for products labeled as “oil-free” or “non-comedogenic.”
-
As mentioned, certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can cause acne.
-
Wearing tight clothing, helmets, or backpacks can cause friction on the skin, which can lead to “mechanical acne” or acne caused by pressure.



